Physician's Notebooks 6 - http://physiciansnotebook.blogspot.com - See Homepage
Chapters 11 to 14. The Chapter 12 is about Exercise and the Heart. Chap. 13 is on Diabetes. Chap 14 is on Fainting & Sudden Death. Scroll down for each - All updated 21 Aug. 2021
Smoking tobacco or marijuana, its effects and affect on the heart and lungs are murderous; it must be avoided for success at long life.11. Smoking and Drinking as Risk Factor in Heart Disease; Drugs; Nutritional Supplements
Stimulants like cocaine, metamphetamines, methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta) and phenylpropanolamine (Commonly in cold meds and cough syrups) cause sudden rises in blood pressure and localized artery spasms. They are all infamous for causing brain strokes mostly from brain hemorrhage and causing myocardial infarction from coronary artery spasm. Excepting Ritalin which doctors find useful in ADHD, these meds should all be avoided.
Opioids (Opium and its derivatives like morphine or heroine) are no harm to the heart. They could be a problem with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease because they reduce the breathing rate. They are useful in relieving stress and can be part of the preventive for coronary artery disease. But because of their illegal status in the United States the obtaining of opioids is risky, expensive and the product may be impure and therefore dangerous.
Ethyl Alcohol (EtOH): Data show EtOH from 1 to 3 drinks a day protects against Coronary Artery Heart Disease. This peaks at 1 drink. At more than 2 a day, other risks from EtOH reverse its benefit. Protection is for older person who already has high risk.
EtOH mildly ups the blood HDL-C - good cholesterol - and also has a mild effect to lower the risk of blood clotting in coronary arteries.
After 15 years of a routine 100 ml wine 2 or 3 times a day, I stopped it because my brain scan MRI showed mild cerebral atrophy in 2014, which may have been an effect from the alcohol drinking. I still occasionally take a social drink when it's offered. Earlier this year, 2021, I again started taking c. 50 ml 37.5% alcohol twice a day in my study eat/drink session. So we shall see?
Nutritional Supplements: According to antioxidant theory, a lack of antioxidants could up risk for heart disease. Important antioxidant food supplements are vitamin C; vitamin E and vitamin A. Tests on large numbers have, surprisingly, shown the vitamin A supplements increase cancer risk and vitamin E supplements increase hemorrhagic stroke risk. Only vitamin C high doses daily shows no harm. My policy is to eat lots of colored vegetables and fruit to get adequate natural vitamin A, and to have grain cereal to get natural vitamin E. For my all-purpose antioxidant I take vitamin C supplement, 2 grams with each meal as powder.
End of Chapter
12. Exercise and the HeartExercise is done best by walking. Walking each day trains the heart to beat slower and causes a better oxygen extraction from blood by heart muscle. Walking is safe, convenient, inexpensive and sustainable. Start walking. Instead of elevator and escalator for going down, use stair; instead of private vehicle, use public transportation, and whenever speed is not needed and distance is not too long, walk.
Have an ‘Edge’ in daily behavior to favor your muscles use.Start new exercise gradually, allowing time to reach max, which is as much as can be done within practical time limit – housework, daily business, travel – by your own effort and give up unnecessary electrical, human and mechanical help.Exercise with Heart Disease: Medically supervised exercise decreases the needs of heart muscle for oxygen at given level of work.
Danger of exercise with Organ Damage: Exercise diverts needed oxygenated, nutrient-rich arterial blood away from vital organs. If the reason for exercise is simply to promote good health, those with poor kidney or liver function or other organ-based disease should not exercise except in a medically supervised program.Exercise and Body Weight: Exercise is an output of body energy and should be balanced against caloric input, the amount of food calories you eat. And the result you see on your balance is your body weight change. Person with low exercise level dies too soon because he eats too much for his level of exercise. Best measure is Body Mass Index. If you can keep BMI below 22, you need not worry about lacking exercise. Just follow the above advice to walk and do functional exercise. What happens to most persons as they age is that caloric eating intake is unchanged while physical activity declines. Result is weight gain, rising BMI and heart disease and premature illness and death. But too late in life an exercise program may be impossible. Then the only alternative is to decrease caloric intake.
Summing up this chapter: walk, walk, walk and you will live long, long, long.
13. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) aka "Diabetes""Diabetes" refers to the excessive urination, and "mellitus", to the urine sweetness that the ancients noted in diabetics. (First noted by their dogs lapping up the urine after a street pee.) The sweet is from glucose which is the basic sugar unit of carbohydrate. In combined form, the sugars make up starches in bread, potato and rice. Important sugars in food are lactose (milk), fructose (fruit) and sucrose (table & cooking sugar). When these are eaten and digested they appear in our system as the single-unit sugar, glucose.
Glucose may be looked on as the purest body fuel. It combines with oxygen in a chemical cycle that energizes our bodies and fuels our brains. The glucose level in artery blood is so important it is carefully controlled.Blood glucose is reported in the U.S. and Japan as milligrams glucose in 100 cc (mg%, or dL). In most of the rest of world it is reported in milliMoles/Liter, or mM/L, blood plasma or serum. The normal overnight fasting blood glucose range in adult vein blood is 74 to 106-mg% (4 to 5.8 mM/L); it goes higher, 120 to 140, (6.6 to 7.7 mM/L) after eating and lower after fasting. When glucose falls below 60 (3.3 mM/L), it may start first a cold sweat and, then a rapid heart and nervousness. Below 40 (2.2 mM/L) you faint and below 20 (1.1 mM/L) is death. Low blood glucose is ‘hypoglycemia; in usual case it is mild and caused by excessive fasting, by alcohol intake without food, or by high protein, low carbohydrate diet. Severe hypoglycemia is from diabetes pills or excess insulin.
The hormone lacking in diabetes, Insulin, is produced by cells in the pancreas. Its action allows glucose from blood plasma to enter the cells, thus preventing the high blood plasma glucose seen in diabetes and allowing the cell to use glucose as energy.
A blood glucose of at least 60 mg% is needed for heart and brain to function normally. There is feedback between blood glucose number and insulin release from pancreas into blood. When glucose falls below 70 mg% (3.85 mM/L), insulin release is shut off and when glucose goes higher than 80 mg% (4.4 mM/L) insulin release is turned on, and it increases with increasing levels of glucose so that blood glucose is kept within normal range.
In diabetes worst case, no insulin can be produced by pancreas because of total destruction of insulin cells. Then body cells cannot use the glucose in blood; instead the body must breakdown proteins and fats into fatty acids. This causes the blood sugar to go high with bad effects; and the body gets filled with ketones and acids (keto-acidosis).
High Blood Glucose (hyperglycemia) is the central sign of diabetes; it makes the diagnosis and explains symptom and complications. When diabetes first gets noticed, the blood glucose may have been gradually rising for months, unnoticed. The first sign of rising glucose is too much urination. The kidneys re-absorb glucose that has passed into excretory tubules; but at the increasing blood glucose levels the kidney re-absorption becomes swamped and glucose appears in urine, where it may be detected by dipstick test.
Glucose in urine pulls water along with it, so the first symptom of a new Diabetes is too much urination and the person starts to drink lots of beverage (A new coke-machine addict!) and goes to the WC to pee too often. Then blood glucose rises so high that the brain stops working normally and the body water, electrolyte and acid-base level is seriously disturbed, and the patient collapses in diabetic keto-acidosis and goes into coma and will die unless treated. This was the fate of most diabetes before insulin, and it still may be in a new case.
Diabetes type I requires insulin injections. It is caused by early-age virus infection or autoimmune disease, which may be genetic.
Diabetes type II is high blood glucose in overweight person usually over age 40. In Type II, the insulin-producing cells are not completely gone and insulin injection treatment may not be needed. Causes of type II are over-eating, under-exercising, partial damage to the insulin-producing part of pancreas, and corticosteroid excess. Also genetic. The high blood glucose in type II is a blunting of response of insulin-producing cell to blood glucose level. The basic treatment of type II is nutritionist-guided weight-loss down to healthy BMI, but often, oral medication or insulin may be needed temporarily.
Type I will become evident by positive test for glucose in urine. Then it can be confirmed by a too high fasting blood glucose or, if the fasting glucose is normal, by a glucose tolerance test where you drink a standard amount of glucose fluid and have blood tested over the next hours. Now a new blood test - the glycosylated hemoglobin - is available. A type of the normal hemoglobin HbA1C is tested for its percentage saturation with the glucose molecule. In normal non diabetics the HbA1C will be 4% to 5.5%. If the test shows 6.5% or higher, it confirms a diagnosis of diabetes. If the test is 5.7% to 6.4% it means the person has a high risk to develop diabetes soon. The HbA1C test is best for type II diabetes. In type I it has a low specificity (i.e., it may be negative and yet the person has diabetes).
It has been shown that persons at risk for diabetes (overweight, cardiovascular disease, HbA1C 5.7 to 6.4%) can prevent getting DM by losing weight to a healthy BMI, lowering the blood test LDL cholesterol by diet and/or a statin drug, and doing more healthy exercise. Mostly these are type II cases.
Complications of diabetes are early and late. High blood glucose is the important early complication more likely to occur sooner in type I Diabetes because of initial episode of high blood glucose that quickly verges into deadly acidosis and coma.
Diabetic Keto-Acidosis is brought on by many stresses and often preceded by gastroenteritis with vomiting or diarrhea. Its shallow breathing and a fruity breath odor make diabetic keto-acidosis easy to mistake for alcoholic stupor with tragic result, because treatment of acute alcoholism may quickly kill a diabetic in coma. (For an interesting fictional account click on 15.11 Scene of a Medical Mistake )
The most obvious difference between a drunk and a diabetic in coma is that the diabetic breathes at rapid rate (more than 20/minute) while the drunk in stupor breathes slowly (less than 12/minute). Also to be considered is that a diabetic may get drunk, in which case the usually rapid respiration may be slowed. Here, one should check for a diabetes ID bracelet or other marker. Also quick dipstick urine test of urine for glucose and low pH.
Late complications of Diabetes equally affect type I and II but, since type I develops at younger age, the late complications have more time to become severe. Important late complications are kidney failure (Most frequent cause for dialysis) ; advanced arterio- and athero-sclerotic heart and blood vessel disease, peripheral nerve disease leading to loss of pain and heat sense in feet with severe infected ulceration and gangrene of lower extremity; or eye retinopathy leading to blindness.
Treatment of Diabetes and Prevention of Complication in types I or II starts with keeping blood glucose 60 – 120 mg% (3.3 to 6.6 mM/L) and HbA1C 6% or less. Every complication of Diabetes is connected to blood sugar going outside the normal range. Central point of treatment is regular, several-time daily finger-stick blood-testing for glucose in order to keep glucose within healthy range. A high HbA1C even with a normal blood glucose means that blood glucose has been too high within the past several weeks. It is a sign of poor treatment in a diabetic.
Lifestyle change: if overweight, lose weight; and, lower LDL cholesterol, increase exercise and eat healthy. These changes should get blood sugar and HbA1C back in normal range.
In type I diabetes, insulin should be used to keep glucose in normal range. There are now many types of insulin, each to suit different needs. The type 1 patient should have initial hospitalization at top diabetes hospital center and get started on correct treatment program by expert team.
In treatment of type II, the patient is usually overweight (BMI>25) and needs weight reduction. This is not simply a weight-reduction diet. It must take into account the affect of particular food (carbohydrate, fat and protein) on blood glucose. The aim of diet in overweight diabetic is to reduce BMI to 20-22 range (ideal BMI individualized based on lowering blood glucose to healthy level and general well being), to get blood lipid to healthy level (LDL cholesterol double-digit mg%, HDL>50 [>1.3 mM/L], and triglyceride in normal range), and to protect kidneys from DM damage. All diabetics should avoid saturated fat, table salt and obviously salted food, keep protein intake high-quality but moderate in amount, and decrease excess caloric intake so that 1 kg weight loss a week is accomplished until stabilization at ideal BMI weight. Also eat high fiber foods and increase moderate exercise.
In type II diabetes without severe high blood glucose, the blood sugar can usually be normalized without insulin injections by using oral hypoglycemic diabetes pills.
At start of diabetes mellitus it is best to seek out expert diabetes team. The self-testing of blood glucose, the treatment decision on what diabetes pill to use, and the proper diet are best learned well at a top center. Follow-up lifetime care can be with local physician.
Tips on self tester: to give highest accuracy 1) If you use antiseptic for finger stick, be sure to allow it to dry before the finger sticking; 2) Wipe off first drop of blood that wells up from the finger stick and use next drop for test sample; 3) Do not compress finger or milk it down before pricking finger.
Not to be neglected is the risk of low blood glucose hypoglycemia from insulin injection or overdose of diabetic pill. Self blood testing before medication will protect against hypoglycemia but also one should be alert to its symptom of drenching sweat, rapid heart and feeling of panic, Chewing candy or eating sugar will counteract hypoglycemia.
About the Oral Hypoglycemics (OH): They lower blood glucose by either stimulating residual insulin-producing pancreatic cell to produce insulin or by affecting liver metabolism to favor lower blood glucose. Used mostly in type II because of residual pancreas capability to produce insulin. Also patients prefer a pill over insulin shots. The decision what diabetes pill to take is best made in cooperation with your expert diabetes team in an HMO or hospital.
Reproduction and Diabetes: Inheritance of diabetes is not absolute because genes interact with behavior. If one parent has it, the risk for child is 2 – 5% for type I and 10 – 15% for type II. If child develops it, the risk that its sibling will develop it is 5 – 10% for type I and 10 – 20% for type II. Usefulness of this data is that when one develops diabetes, his as yet non-diabetic DNA relation should have screening for high blood glucose and be advised to carry out behavior that reduces risk. Women with diabetes who get pregnant carry risk for stillbirth, malformation and large newborn (>8 lbs or >3600 grams) that needs cesarean section. They require extra careful obstetric care and fetal monitoring. As with other complication, the strict control of blood glucose by self-monitoring and careful insulin injection will help prevent obstetric complication.
Self Psychoanalysis: Newly discovered patient often practices psychological denial helped by family, friend and medical adviser. “You can live a perfectly normal life with diabetes” is what one hears and wants to hear. So she or he continues‘enjoying life’ with drinking, smoking, doing drug, engaging in competitive sport and other risky behavior; not being strict about monitoring and controlling blood glucose and weight; and taking oral medicine instead of insulin because of lazy convenience. And such a one dies too fast from stroke, heart, attack; or needs kidney dialysis, amputation, or goes blind; because of not having taken the diabetes seriously enough from discovery. That is why the discovery ought to start self-psychoanalysis. It means educating self about diabetes and body. And telling self, despite others’ reassurance that you have serious, potentially behavior-limiting, life-shortening disease that you can do much for by making major continuing effort to change direction of life. And despite that, maintaining an attitude that you're going to enjoy your life but in a way that does not sicken or shorten it. It comes down to deciding on priority of life. If it is just passing pleasure and "normal life" then you will do as you damn please. But if you want life to have specific goal that needs you to live long and healthily (raising children, writing the novel, inventing useful machine), you will set an aim to keep your weight at healthy level and blood glucose continually in normal range. And at all times you will make an edge against indulging in risk factor behavior for diabetes complication, which means becoming health oriented.
If you are a parent to a child with newly discovered diabetes, you can change a life to make it easier for child to live long and healthily despite the diabetes. It means directing child toward different goal and different future where there will be optimal chance of good health practice and least risk factor.
As already mentioned, diabetes is an additional major risk factor in cardiovascular and kidney disease; so, once you develop it, you want to vigorously prevent these complications by keeping total cholesterol and LDL low, and the HDL high. This means a right dosed statin medication and Omega-3 fish oil capsule. Also even mild hypertension should be treated vigorously. And protect your kidneys by reviewing the chapters in Notebooks 7 on preventing renal failure.
End of Diabetes Chapter
14. Fainting & Sudden DeathAlmost everyone has fainted/collapsed or seen it. No matter the cause, the final link is a lack of oxygen to brain cells. Anyone who begins to feel faint should quickly consider: 1) Lack of oxygen in surrounding air (e.g., aircraft springs a leak to outer air at 36,000 feet); 2) Poison gas that blocks oxygen-use by brain cell (e.g., odorless, colorless carbon monoxide in closed room with electric heater); 3) Drop in Blood Pressure in artery to brain (e.g., fright or other emotional reaction, or heart attack).Less usual cause is sudden arrhythmia of heart including stoppage of heartbeat.One should be alert to impending faint - suddenly pounding fast heart or long missing of heartbeat and cold sweat.Immediate prevention or intervention should be to put self or person about to faint or just fainted, flat on back on firm surface, head level with chest, and arms and legs high as possible above chest. (Increases the return of blood to heart, increases the cardiac output, and blood flow to brain) If the faint is while standing – like most faints – the lying flat position should clear consciousness within seconds. If in situation where one cannot lie down, one should squat down and lower head between knees. And, of course, in whatever way possible call for emergency medical assistance.
Many faints are due to reflex stimulation of the Cranial (Vagus, vaso-vagal) Nerve X, in head-up position due to fright, which makes the vagus nerve slow the heartbeat rate and relax the blood vessel walls, dropping the Blood Pressure. These causes include: standing rigid (usher at ceremony; military at attention) in overheated place, standing up too fast from hot bath; also tight collar, from direct pressure on carotid arteries will cause same. And fear (blood sampling needle stick, close-call injury).Sudden Death: A faint may be the start of sudden death. With first sign of faint, support the person to prevent fall and head trauma; and quickly check breathing and carotid pulse in neck. If recovery not evident within seconds, first immediately call for emergency. Then, if 2 or more persons are there, the one most experienced in Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation and Automated External Defibrillation (CPR &. AED) should attend to the person who is fainting and the other should first call for help and then assist the CPR.Note the breathing by baring the front chest in a person lying flat. Normal breathing rate should not be less than 10 per minute, one breath every 6 seconds.
Appearance of person gives away serious cause of faint: in a fair-skin person, a blue or slate-gray skin color is lack of oxygen. In a colored person, check lips; in anyone, lips a faint cherry red means carbon monoxide poisoning, and giving oxygenated air may be life saving (Also with any low oxygen situation). At least, open window to outer air; and if pure oxygen breathing apparatus available, apply it.
If no heartbeat/pulse, start CPR. If mouth to mouth does not seem to inflate the lungs, suspect blocked airway and at once apply a Heimlich maneuver
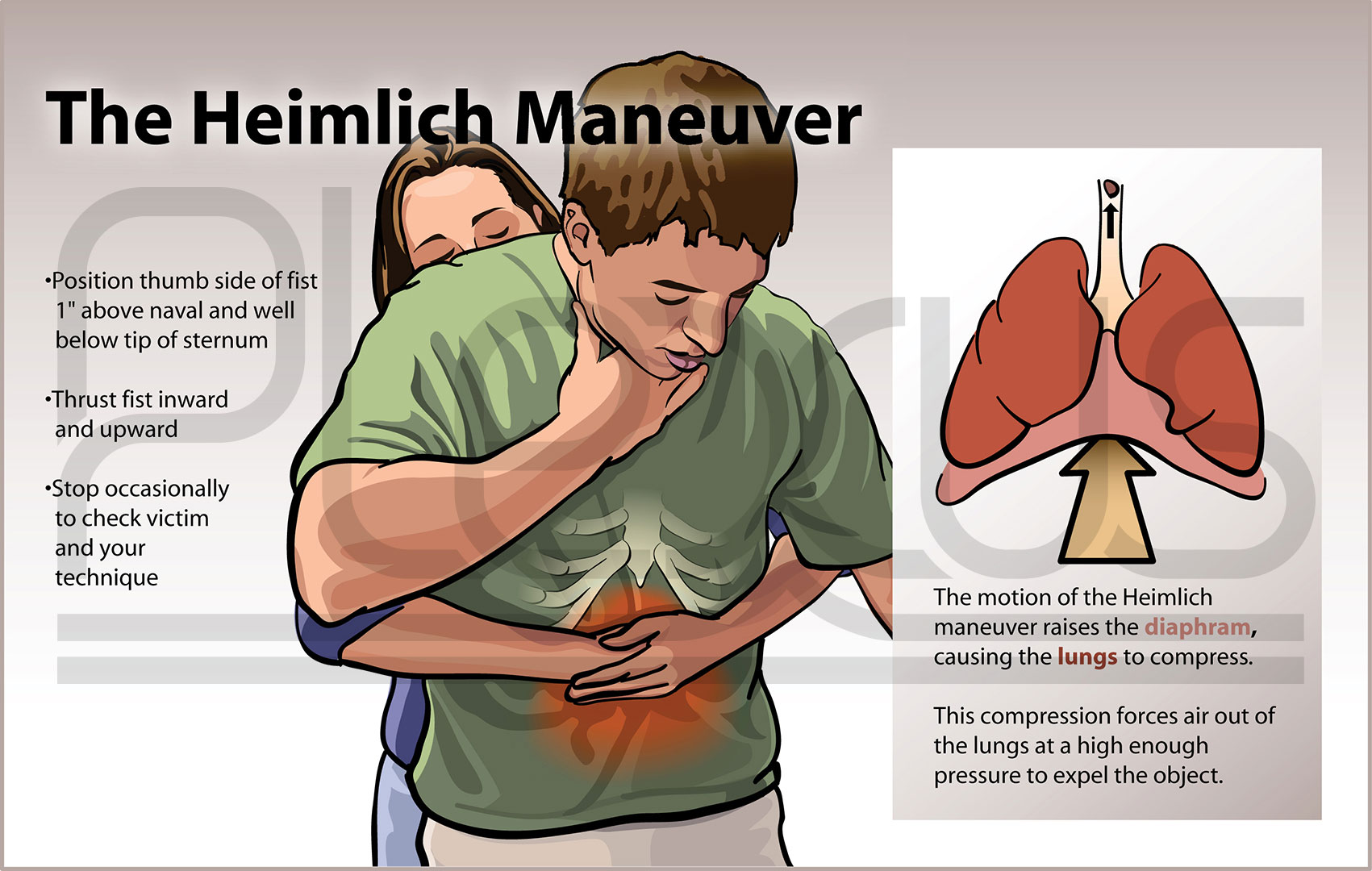
If you don’t know it, learn it; holding the person upright from behind, make sudden strong abdominal pressure at belly-button level with your encircling arms in balled fist point giving sudden crunch to above-bellybutton area and it may eject the airway-blocking object. If the person is lying flat and you can't lift, several sudden strong pushes down with heel of hand on solar plexus area upper mid abdomen just beneath breastbone will accomplish Heimlich. Also pounding with your fist on the mid upper back may dislodge the obstruction.Most obstructions to breathing that need Heimlich maneuver will be obvious from the setting and other symptom. (In restaurant, choking on food with gasping, wheezing, stopping of breath, bluing of skin, person's hand on his throat) But you may come upon the scene with air-block victim simply unconscious with no respiration and irregular, slow or absent pulses.Sudden heart arrhythmia is a serious cause of fainting and sudden death. One can self-suspect it is impending because of awareness of irregular beating of heart (or long missed or skipped beat) and one can diagnose it by palpating carotid artery in neck. Immediately call for assistance. Immediate emergency measure that may save life in case of serious arrhythmia is to give 3 strong punches with balled fist to front of mid chest. If you are the victim of a potentially fatal arrhythmia, making regular strong coughs, 30 to 50 per minute, is another way to bring back normal heart rhythm (and cause effective heart contractions) at start of arrhythmia.
The AED, or automated external defibrillator is now generally available at most locations in U.S.A. and Japan and when a person collapses and no pulses are felt or heartbeats heard, a nearby AED should be sought and used. AEDs give clear simple spoken instruction and can be used without training in case of no heartbeat. But if possible it is best to acquaint oneself with the AED at a quiet moment when no emergency is presenting. The rescuer with most knowledge and experience should be in charge of using AED with CPR. End of Chapters 11 to 14. To read next now, click 6.15 Paul Dudley White Method to Study Hear
2 comments:
I just want to thank you for sharing your information and your site or blog this is simple but nice Information I’ve ever seen i like it i learn something today. Supplement for diabetes singapore
Thanks for Providing A great information.It Is Very helpful for patients.It is really a great post.We At Sweet Clinics Provide Diabetes Treatment ,Complete Diabetes Program,Foot Care In Diabetes,Heart Care In Diabetes,Eye Care In Diabetes , etc.For More Details Visit Us On best diabetes specialist doctor in Navi Mumbai
Post a Comment